
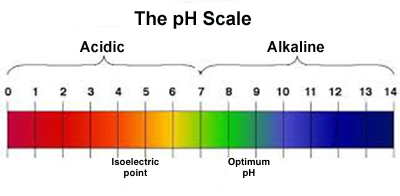
1) Acid: An acid is a substance that releases hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water.

.jpg)



Sodium hydroxide


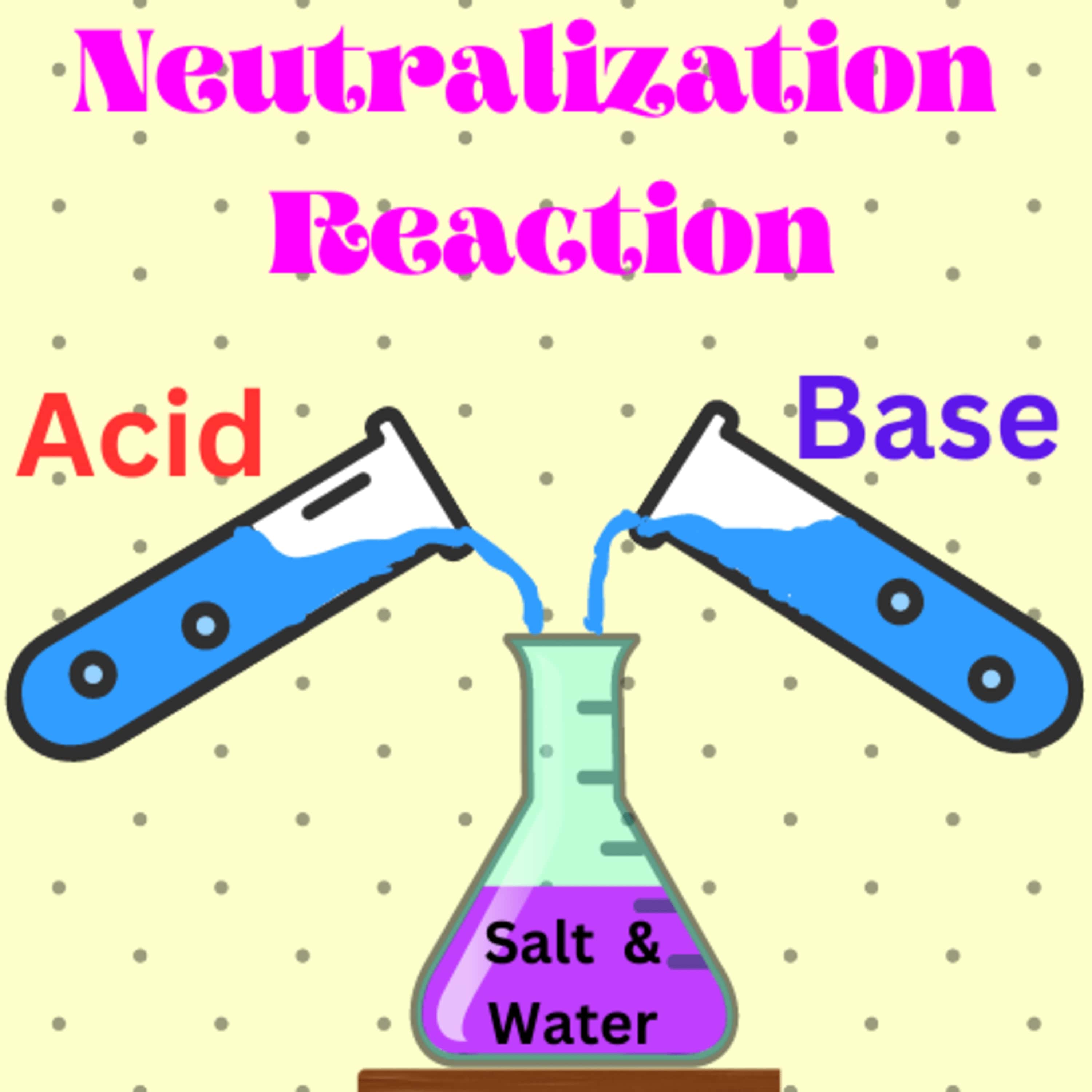
5) Neutralization Reaction: Neutralization is a chemical reaction between
an acid and a base, resulting in the formation of salt and water.
6) Salt: Salt is a compound formed by the reaction
between an acid and a base.
-chloride-hexahydrate-sample.jpg)


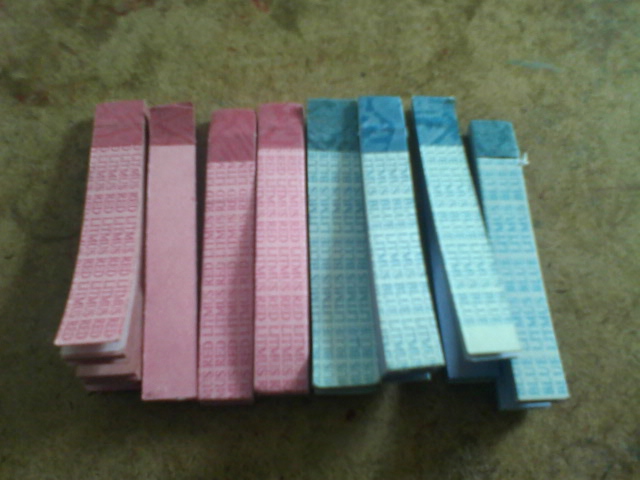
7) Litmus Paper: A pH indicator paper that turns red in the presence of acids and blue in the presence of bases.


8) Litmus solution: A natural indicator extracted from certain
lichens.
9) Amphiprotic Substance: A substance that can act as both an acid and
a base, depending on the conditions. Water is an example of an amphiprotic
substance.


10) Olfactory Indicator: Substances which change their smell when
mixed with acid or base are known as Olfactory Indicators.



11) Synthetic Indicator: Indicators that are synthesized in the
laboratory are known as Synthetic Indicators.

Methyl Orange : Acid - Red , Base - Yellow



Phenolphthalien : Acid - Colourless, Base - Pink




14) Antacid: A base used to get rid of pain and
irritation caused in stomach due to indigestion of food.


15) Aqueous Solution: The solution in which the solvent is water.
16) Brine solution: An aqueous solution of common salt.
17) Dilution: The process of mixing acid or base with
water, to decrease the concentration of ions per unit volume is called
dilution.


No comments:
Post a Comment