
1) Metals: Elements typically solid, shiny, malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity.
.jpg)
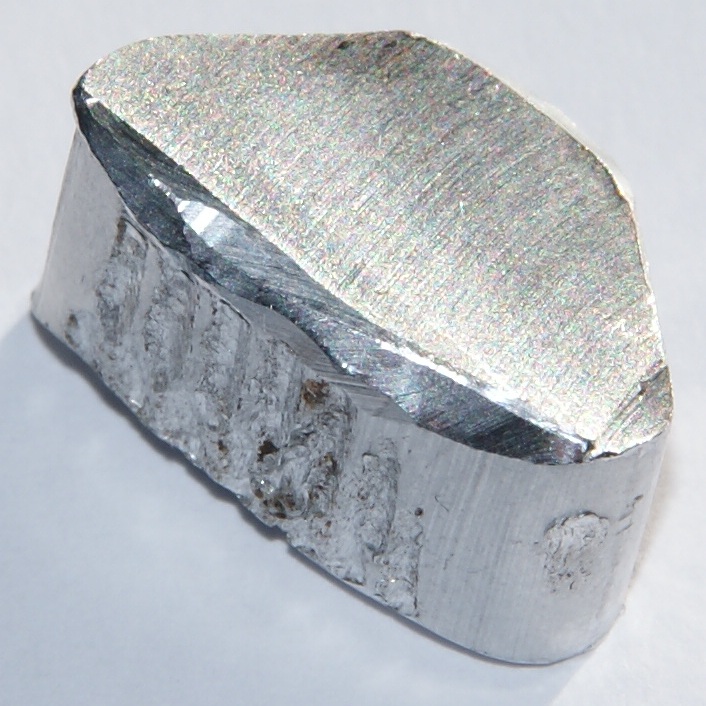
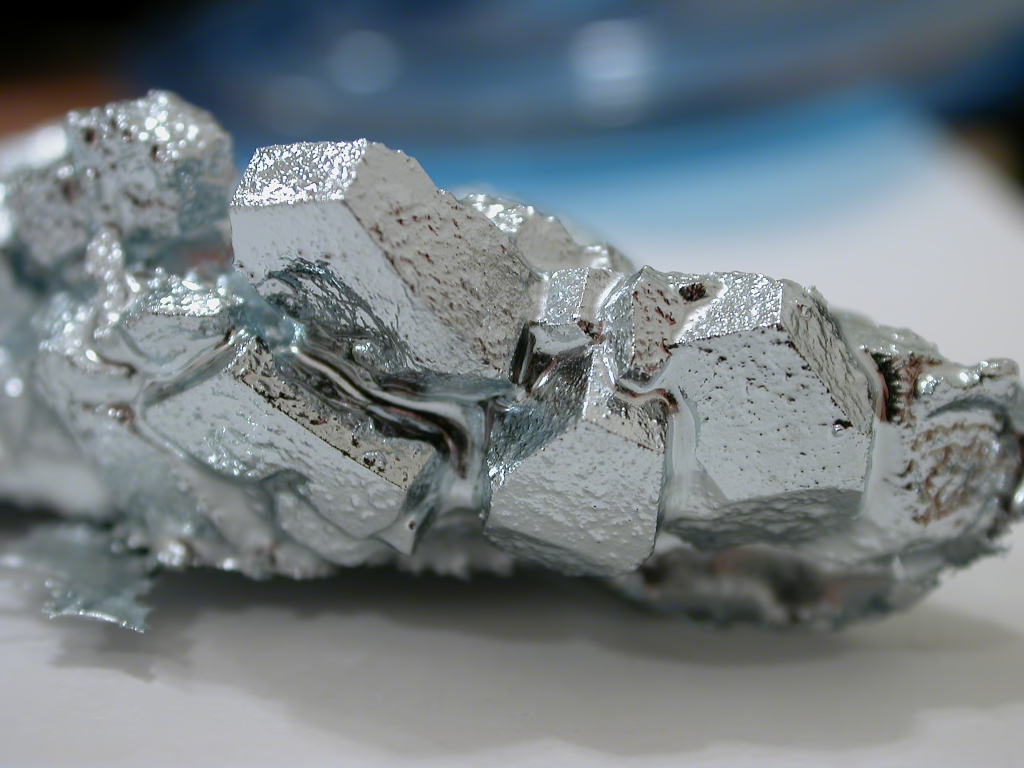





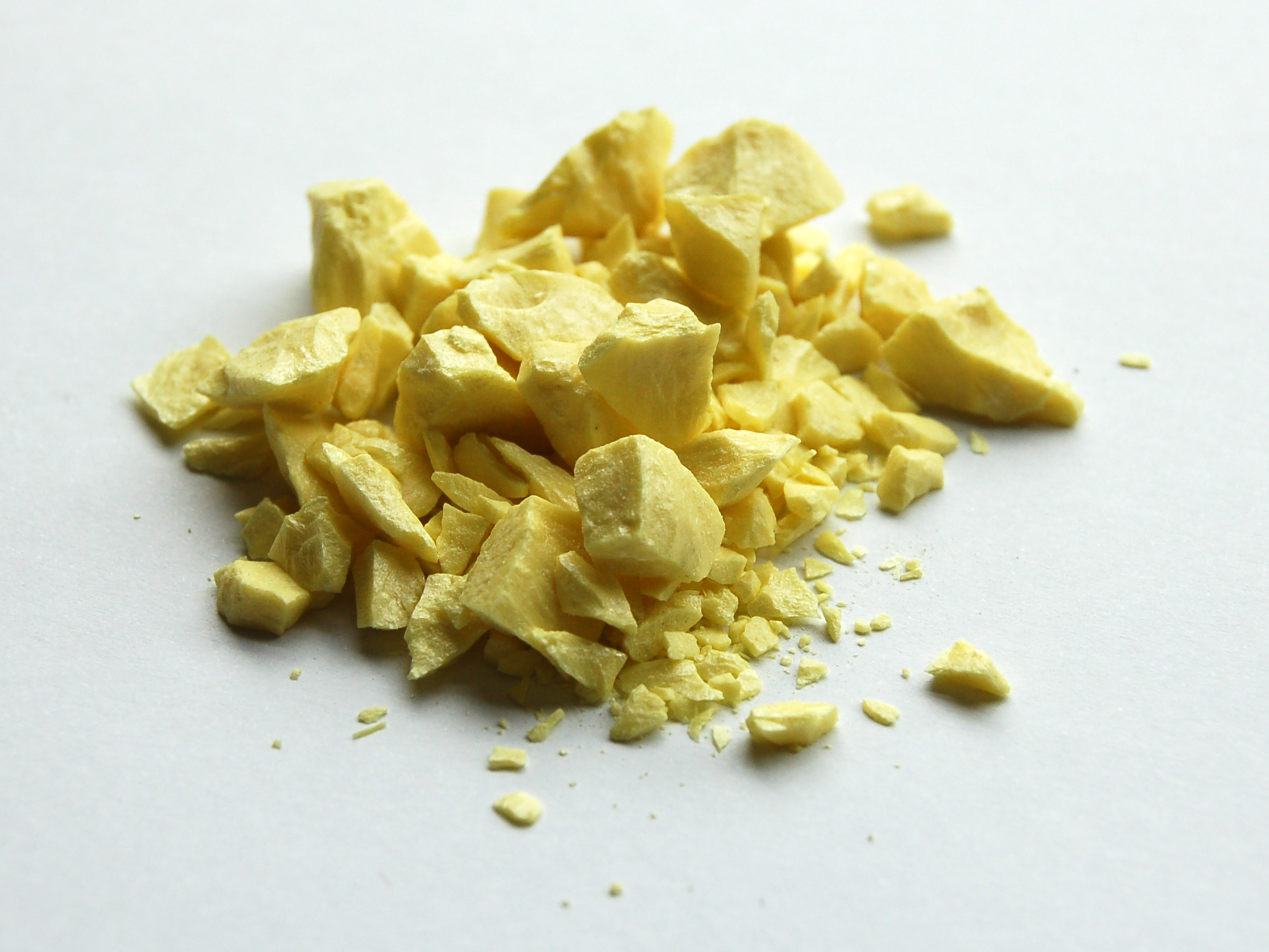
2) Non-Metals: Elements that lack the properties of metals, often being brittle, dull, poor conductors, and exist in various states at room
temperature.




.png)
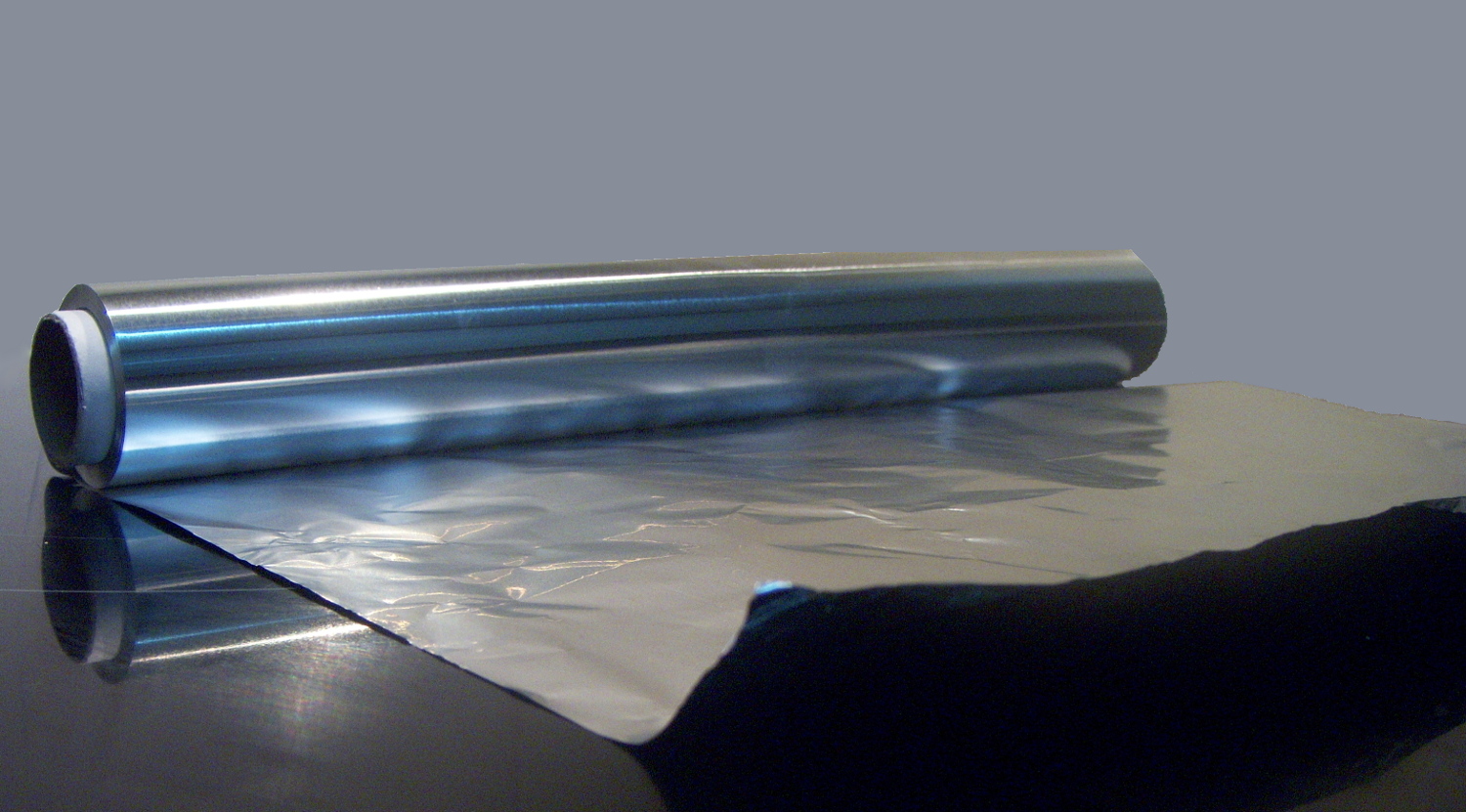
3) Malleability: The property of a material to be hammered or rolled into thin sheets without breaking.
4) Ductility: The property of a material to be drawn into thin wires without breaking.

.jpg)
Copper wire Gold wire
5) Conductivity: The ability of a material to conduct heat or electricity.
6) Luster: The way a material reflects light, often used to describe the shiny appearance of metals.
7) Brittleness: The tendency of a material to shatter or break when subjected to stress.
8) Valence Electrons: Electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom, determining its chemical properties.
9) Ion: Positive or negatively charged atoms are known as ions. Ions are
formed because of the loss or gain of electrons.
10)
Cations: Positively charged ions formed when an atom loses electrons are called as cations.
11)
Anions: Negatively charged ions formed when an atom gains electrons are
called as anions.
12)
Corrosion: The gradual deterioration of metals due to chemical reactions with elements in the environment, such as oxygen and
moisture.
13) Oxidation: The process where a substance loses electrons, often involving the addition of oxygen.
14) Reduction: The process where a substance gains electrons, often involving the removal of oxygen.
15)
Alloy: A mixture of two or more elements, with at least one being a metal, resulting in enhanced properties.
16)
Galvanization: To protect steel and iron from rusting, a thin layer of zinc is coated on them, this is known as Galvanization.
17) Noble Gases: Group 18 elements in the periodic table, which are inert and generally do not react with other elements.
18) Metalloids: Elements with properties intermediate between metals and non-metals, such as silicon and boron.
19) Periodic Table: A chart that organizes elements based on their atomic number, properties, and electronic configuration.
20) Mineral: Minerals are naturally occurring substances that have a uniform composition.
21) Ores: The minerals from which a metal can be profitably extracted are called Ores.
22)
Gangue: Gangue means the impurities present in the ore.





No comments:
Post a Comment